What is active learning?
Active learning is a teaching method that emphasizes involvement and participation in the learning process. In active learning, learners are actively engaged in their own learning, rather than simply receiving information from a teacher, coach, or instructor. This can involve a variety of activities, such as problem-solving, discussions, debates, and hands-on experiments.
Active learning is based on the idea that people learn best when they are actively engaged in the learning process, rather than simply passively receiving information. By participating in activities and discussions, students are able to apply what they are learning, think critically, and develop a deeper understanding of the material.
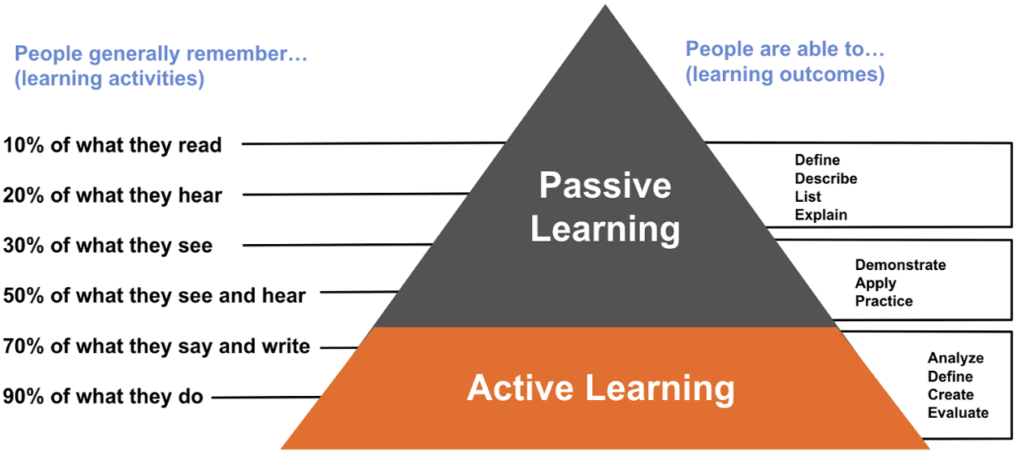
Active learning > passive learning
There are several reasons why active learning is better than passive learning:
- Active learning promotes student involvement and participation: In active learning, students are actively engaged in their own learning, rather than simply receiving information from a teacher or instructor. This allows students to be more involved in the learning process, and to apply what they are learning in a hands-on, practical way.
- Active learning promotes critical thinking and problem-solving: By participating in activities and discussions, students can develop their critical thinking and problem-solving skills, which are essential for learning and personal growth. Active learning encourages students to think critically about the material they are learning, and to develop creative solutions to problems.
- Active learning provides opportunities for collaboration and networking: Active learning often involves collaboration and networking with other students and experts. This can provide valuable opportunities for students to learn from each other, to share experiences and ideas, and to build relationships with other learners and experts in their field.
- Active learning leads to better retention and understanding of the material: Research has shown that active learning leads to better retention and understanding of the material, compared to passive learning. By actively engaging with the material, students are more likely to remember and understand what they are learning, and to be able to apply it in real-world situations.
Active learning is better than passive learning because it promotes involvement and participation, promotes critical thinking and problem-solving, provides opportunities for collaboration and networking, and leads to better retention and understanding of the material.
Why active learning can be difficult
While active learning can be an effective and beneficial way to learn, it can sometimes be difficult to engage in. Some of the reasons why it may be difficult to engage in active learning include:
- Lack of time: Engaging in active learning often requires students to spend more time on their learning than they would if they were simply passively consuming content. This can be challenging for students who have busy schedules and may not have the time to devote to actively engaging with the material.
- Fear of failure: For some students, the prospect of actively participating in discussions or activities can be intimidating, as it can involve the risk of failure or embarrassment. This fear of failure can prevent students from fully engaging in active learning, and may hold them back from participating in discussions or activities.
- Limited access to resources: In some cases, students may not have access to the resources or support they need to engage in active learning. For example, they may not have access to the necessary equipment or materials for hands-on activities, or may not have access to mentors or experts who can provide guidance and support.
- Poorly designed or implemented active learning activities: In some cases, active learning activities may be poorly designed or implemented, which can make it difficult for students to engage in them. For example, the activities may not be aligned with the material, may be too difficult or too easy, or may not provide students with the necessary support and guidance to be successful.
While active learning can be an effective and beneficial way to learn, it can sometimes be difficult to engage in. By addressing these challenges and obstacles, students can more fully engage in active learning and reap its benefits.
Examples of active learning
There are many different examples of active learning, which can take a variety of forms depending on the subject area and the specific learning objectives.
Some examples of active learning include:
- Problem-based learning: In problem-based learning, students work in small groups to solve real-world problems. This can involve researching the problem, developing solutions, and presenting their findings to the class.
- Project-based learning: In project-based learning, students work on a long-term project that involves researching a topic, developing a product or solution, and presenting their findings to the class.
- Discussion-based learning: In discussion-based learning, students engage in discussions and debates about the material they are learning. This can involve asking questions, sharing ideas, and listening to and responding to the ideas of others.
- Hands-on activities: Hands-on activities involve students completing hands-on tasks or experiments related to the material they are learning. This can involve conducting experiments, building models, or working with technology or other equipment.
There are many different examples of active learning, which can take a variety of forms depending on the subject area and the specific learning objectives. By engaging in active learning, students can develop their critical thinking, problem-solving, and collaboration skills, and can better understand and retain the material they are learning.



